Fibrous Areolar Adipose Reticular and Dense includes material that helps bind skin muscles bone and other organs together. Contains primarily lymphocytes mast.
Connective Tissues Functions Types Characteristics Components Connective Tissue Cells Fibers
Connective tissue as the name suggests are the group of tissues which supports connects binds or separates other organs or tissues in the body.
. Epithelial tissue refers to groups of cells that cover the exterior surfaces of the body line internal cavities and passageways and form certain glands. Connective tissue has three main components. 2 Kinds of Connective Tissue.
Muscle tissue contracts forcefully when excited providing movement. Functions of the Areolar Connective Tissue. Hard arranged in osteons or network of beams.
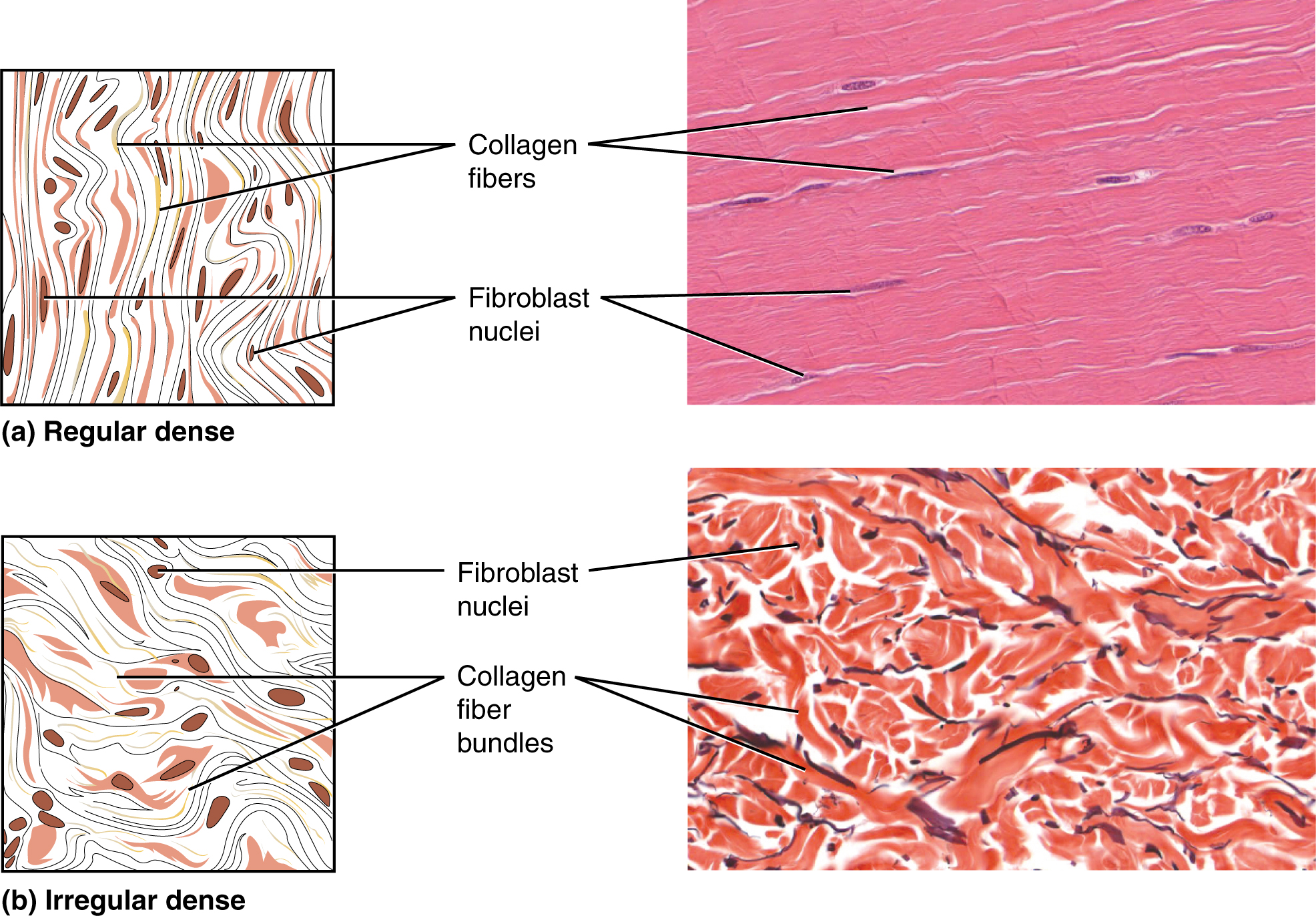
Cells contain processes that receive and generate electrical signals to communicate with other cells. Connective tissue as its name implies binds the cells and organs of the body together and functions in the protection support and integration of all parts of the body. This micrograph shows hyaline cartilage a semi-rigid connective tissue from a human trachea windpipe.
Fibers and Cells BR 1. It is among one of the four basic cells of the animal body. Tissue contains more extracellular matrix than cells.
Loose arrangement of collagen elastic and cells. Skin Surface- epithelial tissue Fat- connective tissue spinal cord- Nervous tissue Heart tissue- muscular tissue blood- Connective tissue inner lining of the stomach- epithelial tissue. The other three are nervous muscle and epithelial tissue.
Fibroblast connective tissue proper. The Four Types of Tissues. Soft and specialized connective tissue.
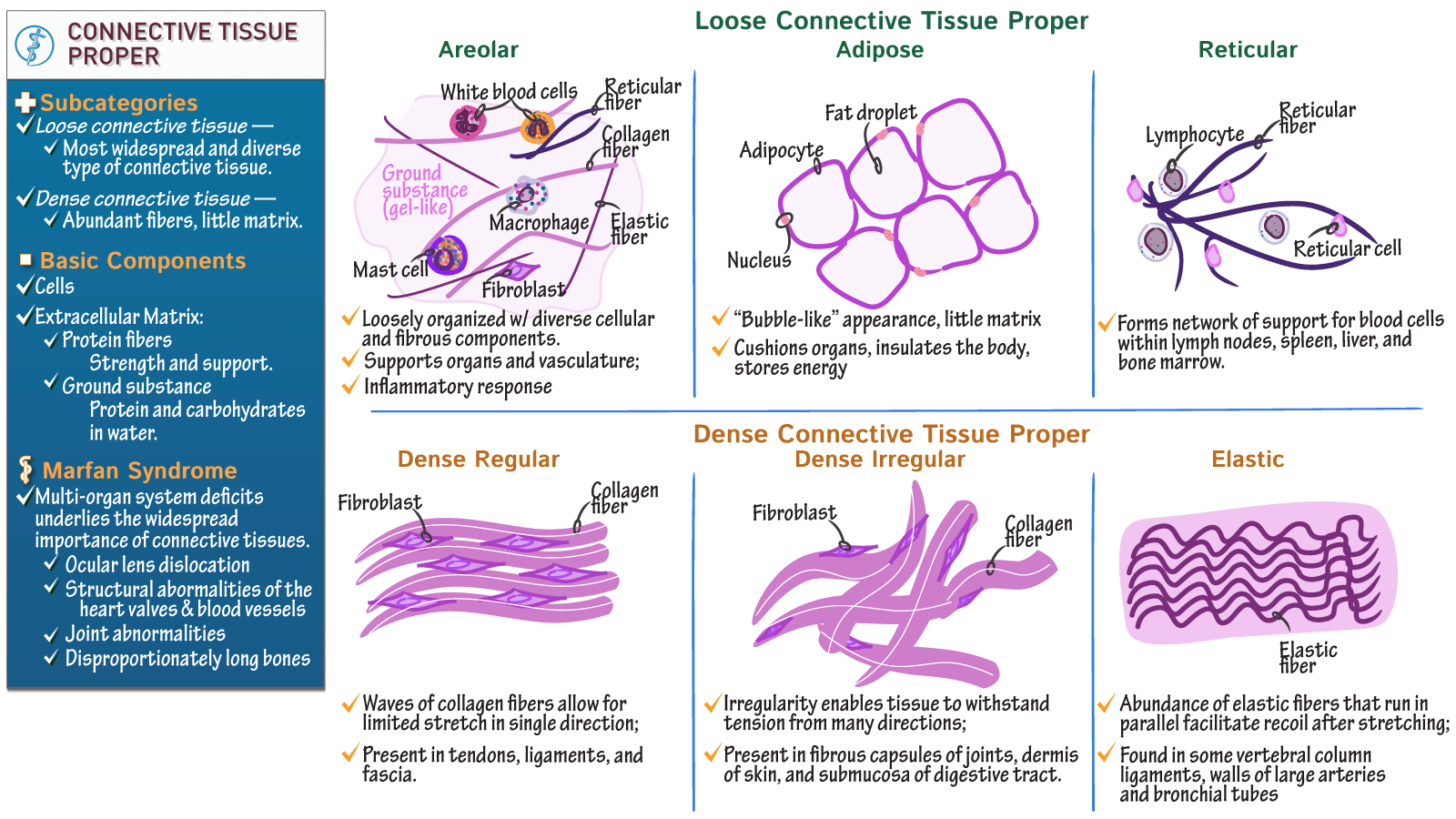
Very thin collagenous fibers. Connective tissue has two subclasses namely loose and dense tissues. The Four Primary Tissue Types.
Loose connective tissue consists of thin loosely arranged collagen fibers in a viscous ground substance. Collagen fibers elastic fibers and reticular fibers. Epithelial tissue also referred to as epithelium refers to the sheets of cells that cover exterior surfaces of the body lines internal cavities and passageways and forms certain glands.
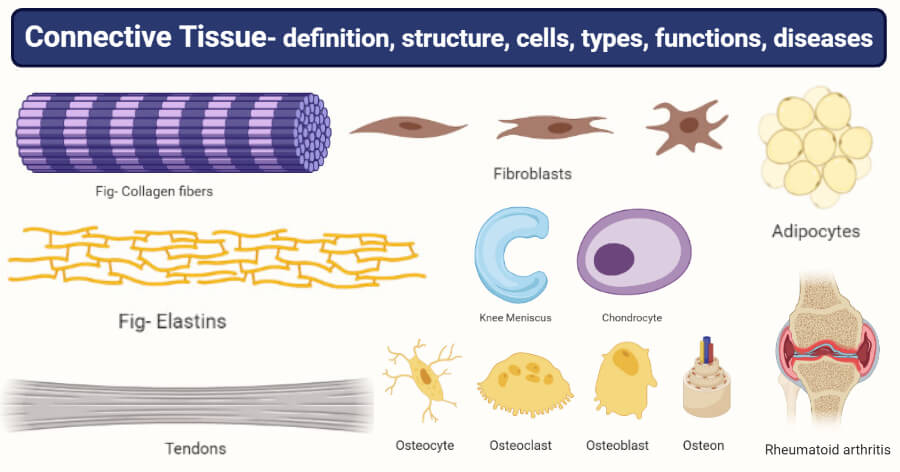
Cells fibers and ground substance. Blood cartilage adipose bone are all. The primary cell type of connective tissue proper is the fibroblast which secretes the ground substance and protein fibers in the extracellular matrix.
Name the two major components of matrix and if applicable subclasses of each component. Connective tissue proper two types. Adipose tissue is a form of loose connective tissue that stores fat.
Connective tissue develops from an embryonic type of tissue that is made up of undifferentiated cells known as mesoderm and its main purpose is to give and maintain the structure of our organs. Connective tissue as its name implies binds the cells and organs of the body together and functions in the protection support and integration of all parts of the body. Name and describe the primary connective tissues.
Connective tissue is a tissue that holds the cells together. The three main types of cell found in connective tissue are fibroblasts macrophages and mast cells. As the name suggest connective tissue is a tissue that connects the different cell and structure of the body.
The primary cell of connective tissue is the fibroblast. Cells and stem cells. In addition it has a mesodermal origin that consists of various.
Three main types of fibers are secreted by fibroblasts. Together the ground substance and fibers make up the extracellular matrix. Connective tissue notes 2.
Start connective tissue lab turn in. This micrograph shows. Proper connective tissues include loose connective tissue often referred to as areolar tissue and dense connective tissue.
Protein fibers dominated by reticulin a highly branched support structure. Connective tissue is classified into two subtypes. Areolar tissues are widely distributed in the body and primarily function as a packing material between other tissues.
Hard flexible gel matrix with embedded chondrocytes. Also these tissues perform other function that helps in the various mechanism of the body. Adipose lines organs and body.
What is Areolar Connective Tissue. B Adipose Tissue storehouse for nutrients packed with cells and blood vessels c Reticular Connective Tissue internal supporting framework of some organs delicate network of fibers and cells 2 Dense. 1 Loose Connective Tissue.
Tissue has elongated cells that shorten and cause movement. A Areolar Connective Tissue cushion around organs loose arrangement of cells and fibers. It functions both mechanically and metabolically.
It binds supports and anchors cells and tissues and it. Fibroblasts produce the fibers of the matrix macrophages scavenge the tissue as an immune cell while mast cells release heparin and histamine in response to stress. They support and link different tissues and organs.
Connective tissue is the most abundant and widely distributed of the primary tissues. Besides fibroblasts several other cell types are present. Name the primary tissue type epithelial connective muscle or nervous that is described.
Dense connective tissue subtypes. Immune supporting tissue found in bone marrow. Connective tissue as its name implies binds the cells and organs of the body together.
Name and describe the primary connective tissues. Name the primary cell type in connective tissue proper. Its function is to produce and maintain the ECM of connective tissue.
Connectives tissues are the most abundant tissues found in the body. For example tendon is a connective tissue which connects muscle to bone ligament is connective tissue that connects one bone with another bone. The Four Types of Tissues.
The six types of connective tissue are bones cartilage and loose connective tissue and adipose tissue dense regular and irregular connective tissues. Connective tissue proper is the largest category of connective tissue. Loose connective tissue subtypes.
These are the cells of the immune system macrophages lymphocytes and mast cells and adipocytes. Liquid matrix with flowing red and white cells. Loose connective tissues are further classified into areolar adipose and reticular tissue.
Epithelial tissue also referred to as epithelium refers to the sheets of cells that cover exterior surfaces of the body lines internal cavities and passageways and forms certain glands. Specialized Connective Tissues Adipose Tissue. For example tendons are strong cables or bands of connective tissue that attach muscles to bone and ligaments are connective tissue bands that hold bones together Supporting and Moving -Bones of the skeletal system provide rigid support for the body and the semirigid cartilage supports structures such as the nose ears and surfaces of joints.
They provide nourishment stability strength and support to various organs of the body.
Connective Tissue Definition Structure Cells Types Functions Diseases

Connective Tissue Supports And Protects Anatomy And Physiology
0 Comments